AMOC Publication Figures
This notebook demonstrates how to create publication-quality AMOC figures using the AMOCatlas package with PyGMT. It reproduces plots similar to those in Frajka-Williams et al. (2019, 2023) and other AMOC publications.
Features:
Clean, simplified workflow using amocatlas module functions
Publication-quality PyGMT plots
Multi-array time series comparison
Tukey filtering for low-frequency analysis
Component breakdown plots (e.g., RAPID, OSNAP)
Figures are designed to be re-used: the “AMOCatlas” badge and timestamp can be cropped out.
Suggested citation:
For the multi-panel figure, you can say “updated from Frajka-Williams et al. 2019”.
[1]:
import os
# AMOCatlas imports
from amocatlas import read, tools, plotters
# Set GMT library path if needed (adjust for your system)
# os.environ["GMT_LIBRARY_PATH"] = "/opt/homebrew/lib" # macOS Homebrew
# os.environ["GMT_LIBRARY_PATH"] = "/usr/lib" # Linux
# Create figures directory for documentation
figures_dir = "../docs/source/_static/paperfigs"
os.makedirs(figures_dir, exist_ok=True)
print(f"✓ Figures will be saved to: {figures_dir}/")
✓ Figures will be saved to: ../docs/source/_static/paperfigs/
1. Load and Standardize Data
Load MOC data from all major observing arrays and convert to standardized format.
[2]:
# Load datasets
print("Loading AMOC array datasets...")
# RAPID 26°N
rapid_std = read.rapid(all_files=True)
# MOVE 16°N
move_std = read.move()
# OSNAP Subpolar
osnap_std = read.osnap(transport_only=True)
# SAMBA 34.5°S
samba_std = read.samba(all_files=True)
print("✓ All datasets loaded and standardized")
Loading AMOC array datasets...
Loading 5 RAPID 26°N dataset(s):
0. moc_transports.nc: RAPID layer transport time series
1. moc_vertical.nc: RAPID vertical streamfunction time series
2. ts_gridded.nc: RAPID gridded temperature and salinity
3. 2d_gridded.nc: RAPID 2D gridded data
4. meridional_transports.nc: RAPID meridional transport data
Loading 1 MOVE 16°N dataset(s):
0. OS_MOVE_20000206-20221014_DPR_VOLUMETRANSPORT.nc: MOVE transport time series
Loading 1 OSNAP dataset(s):
0. OSNAP_MOC_MHT_MFT_TimeSeries_201408_202207_2025.nc: Time series of MOC, MHT, and MFT (2014-2022)
Loading 2 SAMBA 34.5°S dataset(s):
0. Upper_Abyssal_Transport_Anomalies.txt: Daily volume transport anomaly estimates for the upper and abyssal cells of the MOC
1. MOC_TotalAnomaly_and_constituents.asc: Daily travel time values, calibrated to a nominal pressure of 1000 dbar, and bottom pressures from the two PIES/CPIES moorings
✓ All datasets loaded and standardized
2. Extract Time Series to Pandas DataFrames
Convert xarray datasets to pandas DataFrames for filtering and PyGMT plotting.
[3]:
# Extract time series using new tools functions
rapid_df = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(rapid_std[0])
rapid_df["moc"] = rapid_std[0]["MOC"].values
move_df = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(move_std)
move_df["moc"] = -move_std["MOC"].values # Sign correction
osnap_df = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(osnap_std)
osnap_df["moc"] = osnap_std["MOC_SIGMA0"].values
samba_df = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(samba_std[1]) # Use dataset [1] for MOC
samba_df["moc"] = samba_std[1]["MOC"].values
print("Time series extracted:")
print(f" RAPID: {len(rapid_df)} points")
print(f" MOVE: {len(move_df)} points")
print(f" OSNAP: {len(osnap_df)} points")
print(f" SAMBA: {len(samba_df)} points")
Time series extracted:
RAPID: 14599 points
MOVE: 4164 points
OSNAP: 96 points
SAMBA: 2964 points
3. Bin Data to Monthly Resolution
Ensure consistent temporal resolution across arrays for comparison.
[4]:
# Bin to monthly resolution if needed
rapid_binned = tools.check_and_bin(rapid_df)
move_binned = tools.check_and_bin(move_df)
osnap_binned = tools.check_and_bin(osnap_df)
samba_binned = tools.check_and_bin(samba_df)
# Handle SAMBA temporal gaps to prevent plotting artifacts
samba_binned = tools.handle_samba_gaps(samba_binned)
print("✓ Data binned to consistent temporal resolution")
print("✓ SAMBA gaps handled to prevent plotting artifacts")
✓ Data binned to consistent temporal resolution
✓ SAMBA gaps handled to prevent plotting artifacts
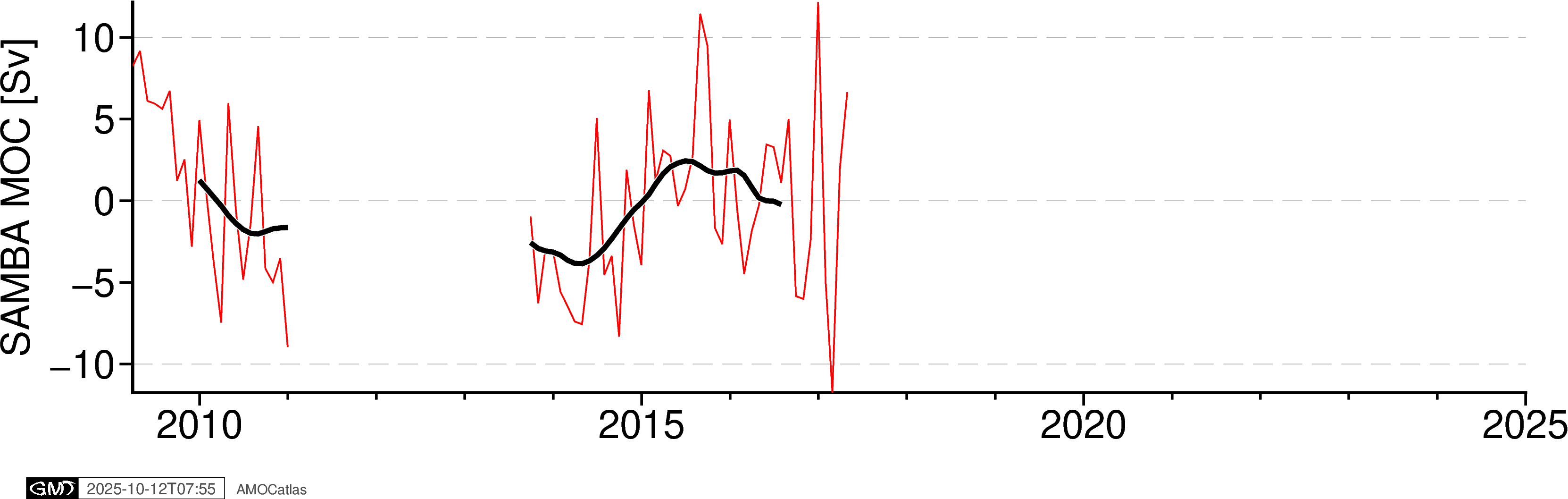
Special Handling for SAMBA Data
SAMBA MOC data contains significant temporal gaps (e.g., 2011-2014) that can cause plotting artifacts. PyGMT and other plotting functions connect all valid (non-NaN) data points regardless of temporal gaps, creating spurious lines across missing periods. The tools.handle_samba_gaps() function prevents these artifacts by:
Creating a regular monthly time grid
Preserving NaN values where no original data existed
Only allowing interpolation within continuous data segments
This ensures clean plots without false connections across data gaps.
4. Apply Tukey Filtering
Apply 18-month Tukey filter to highlight low-frequency variability.
[5]:
# Apply 18-month Tukey filter for low-frequency analysis
filter_params = {"window_months": 18, "samples_per_day": 1/30, "alpha": 0.5}
rapid_filtered = tools.apply_tukey_filter(rapid_binned, column="moc", **filter_params)
move_filtered = tools.apply_tukey_filter(move_binned, column="moc", **filter_params)
osnap_filtered = tools.apply_tukey_filter(osnap_binned, column="moc", **filter_params)
samba_filtered = tools.apply_tukey_filter(samba_binned, column="moc", **filter_params)
print("✓ Tukey filtering applied (18-month window)")
✓ Tukey filtering applied (18-month window)
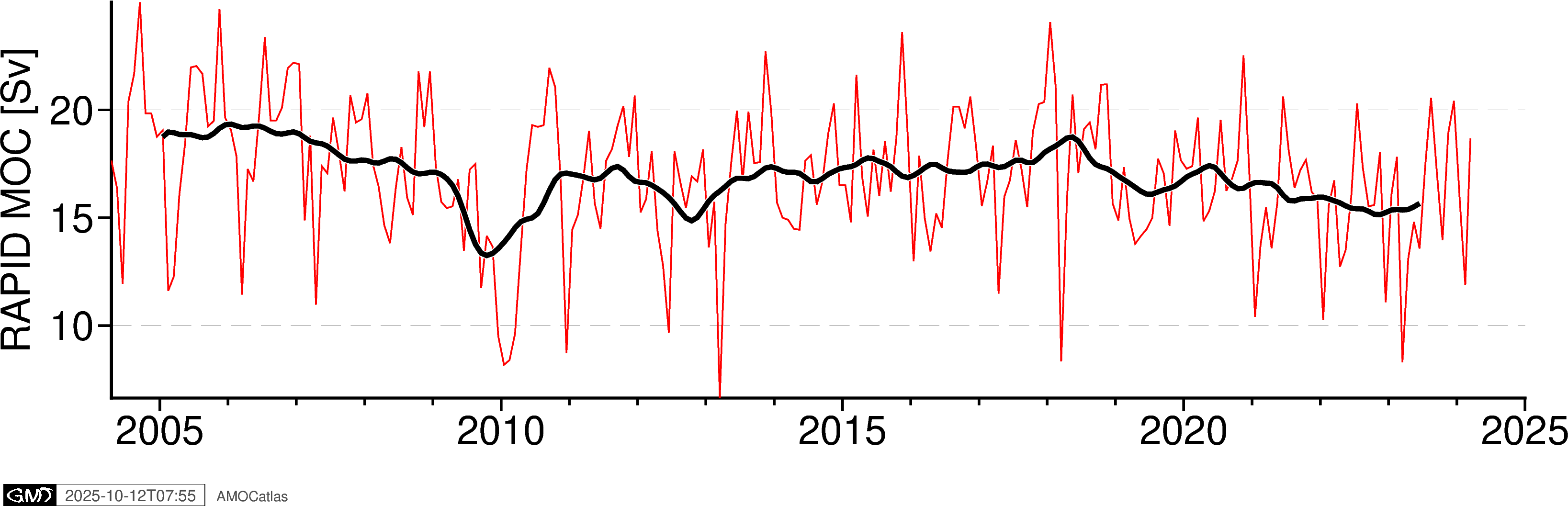
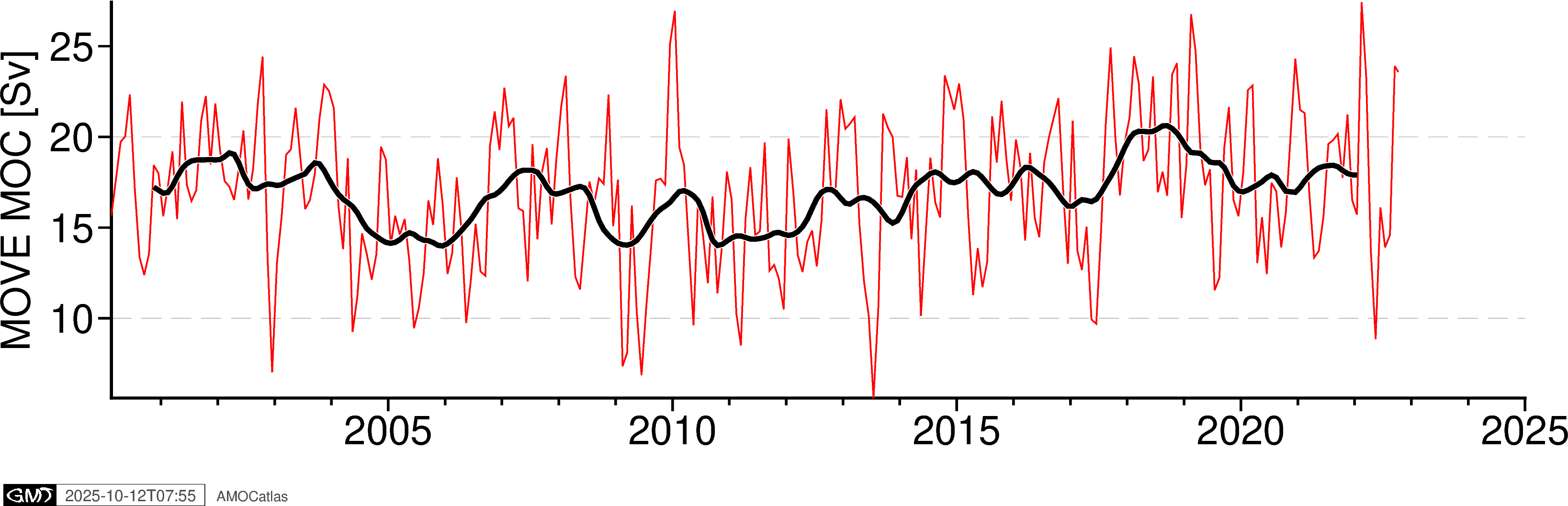
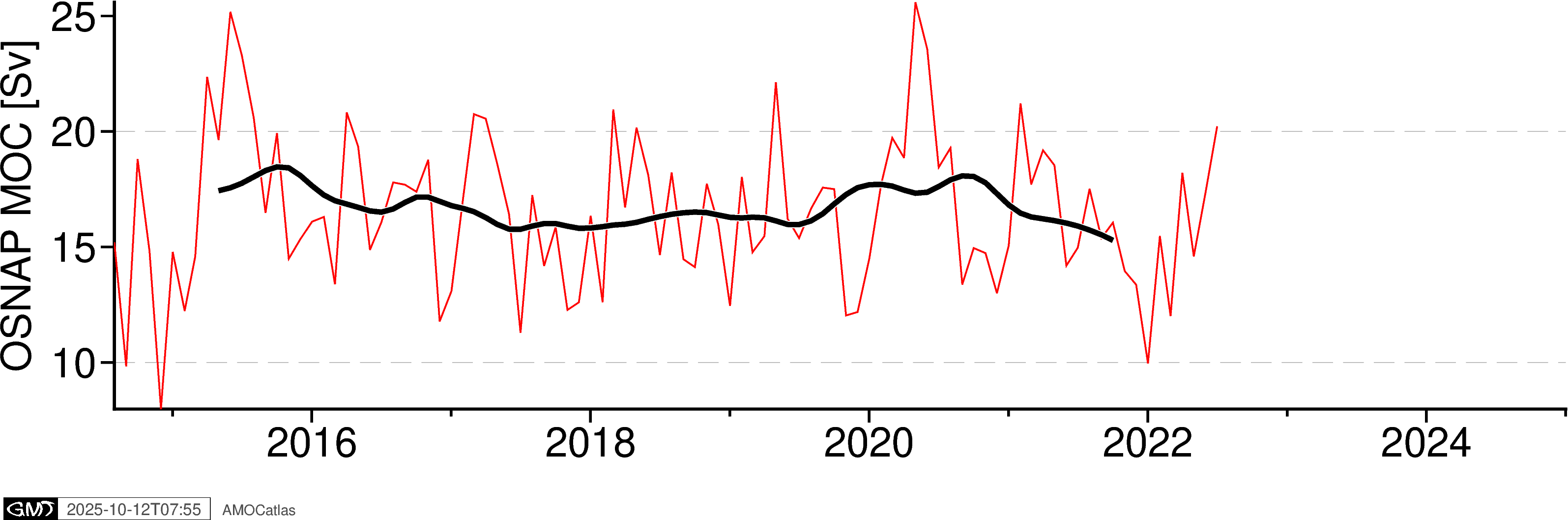
5. Single Array Time Series Plots
Create individual time series plots for each array.
[6]:
# Individual time series plots
try:
fig_rapid = plotters.plot_moc_timeseries_pygmt(rapid_filtered, label="RAPID MOC [Sv]")
fig_rapid.show()
fig_move = plotters.plot_moc_timeseries_pygmt(move_filtered, label="MOVE MOC [Sv]")
fig_move.show()
fig_osnap = plotters.plot_moc_timeseries_pygmt(osnap_filtered, label="OSNAP MOC [Sv]")
fig_osnap.show()
fig_samba = plotters.plot_moc_timeseries_pygmt(samba_filtered, label="SAMBA MOC [Sv]")
fig_samba.show()
except ImportError as e:
print(f"PyGMT not available: {e}")
print("Install with: pip install pygmt")
[7]:
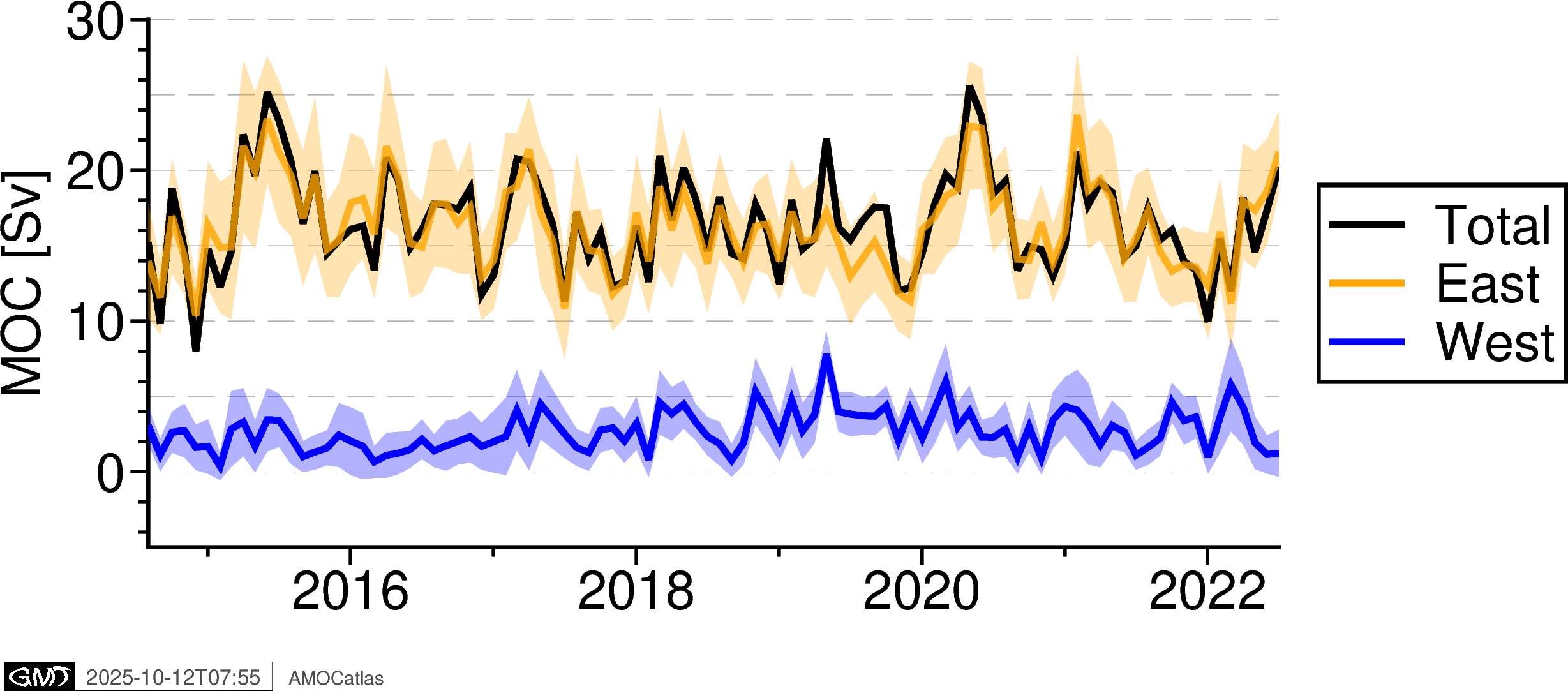
# OSNAP components plot with error bands
try:
# Extract OSNAP component data
ds = osnap_std
osnap_components = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(ds)
# Add all OSNAP variables
for var in ["MOC_SIGMA0", "MOC_SIGMA0_ERR", "MOC_EAST_SIGMA0", "MOC_EAST_SIGMA0_ERR",
"MOC_WEST_SIGMA0", "MOC_WEST_SIGMA0_ERR"]:
osnap_components[var] = ds[var].values
fig_osnap_comp = plotters.plot_osnap_components_pygmt(osnap_components)
fig_osnap_comp.show()
# Optional: save high-resolution version
# fig_path = os.path.join(figures_dir, "osnap_components.png")
# fig_osnap_comp.savefig(fig_path, dpi=300, transparent=True)
# print(f"✓ Saved: {fig_path}")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"PyGMT not available: {e}")
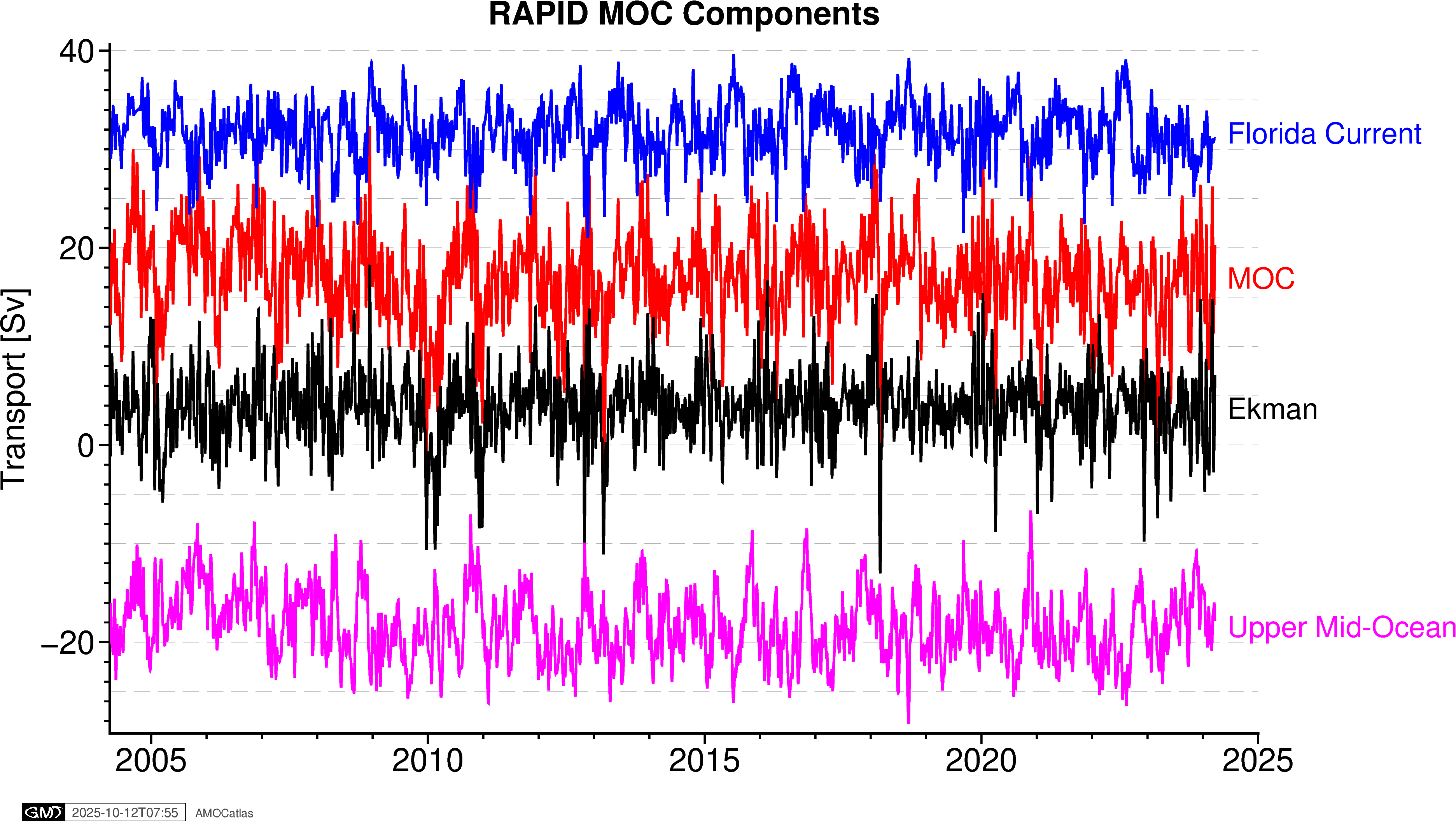
6. RAPID components plot
[8]:
# RAPID components plot
try:
# Extract RAPID component data
ds = rapid_std[0]
rapid_components = tools.extract_time_and_time_num(ds)
# Add transport components
rapid_components["moc_mar_hc10"] = ds["MOC"].values
rapid_components["t_gs10"] = ds["TRANS_FC"].values # Florida Current
rapid_components["t_ek10"] = ds["TRANS_EKMAN"].values # Ekman
rapid_components["t_umo10"] = ds["TRANS_UMO"].values # Upper Mid-Ocean
fig_rapid_comp = plotters.plot_rapid_components_pygmt(rapid_components)
fig_rapid_comp.show()
except ImportError as e:
print(f"PyGMT not available: {e}")
7. Multi-array comparison plot - original data
try: fig_multi = plotters.plot_all_moc_pygmt( osnap_filtered, rapid_filtered, move_filtered, samba_filtered, filtered=False ) fig_multi.show()
# Save high-resolution version
fig_path = os.path.join(figures_dir, "amoc_multi_array.png")
fig_multi.savefig(fig_path, dpi=300, transparent=True)
print(f"✓ Saved: {fig_path}")
except ImportError as e: print(f”PyGMT not available: {e}”)
[9]:
# Multi-array comparison plot - filtered data
try:
fig_multi_filt = plotters.plot_all_moc_pygmt(
osnap_binned, rapid_binned, move_binned, samba_binned,
filtered=False
)
fig_multi_filt.show()
# Save high-resolution version
fig_path = os.path.join(figures_dir, "amoc_multi_array.png")
fig_multi_filt.savefig(fig_path, dpi=300, transparent=True)
print(f"✓ Saved: {fig_path}")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"PyGMT not available: {e}")

✓ Saved: ../docs/source/_static/paperfigs/amoc_multi_array.png
[10]:
# Or overlaid, with SAMBA offset because it's an anomaly
fig_overlaid = plotters.plot_all_moc_overlaid_pygmt(
osnap_filtered, rapid_filtered, move_filtered, samba_filtered,
filtered=True
)
fig_overlaid.show()
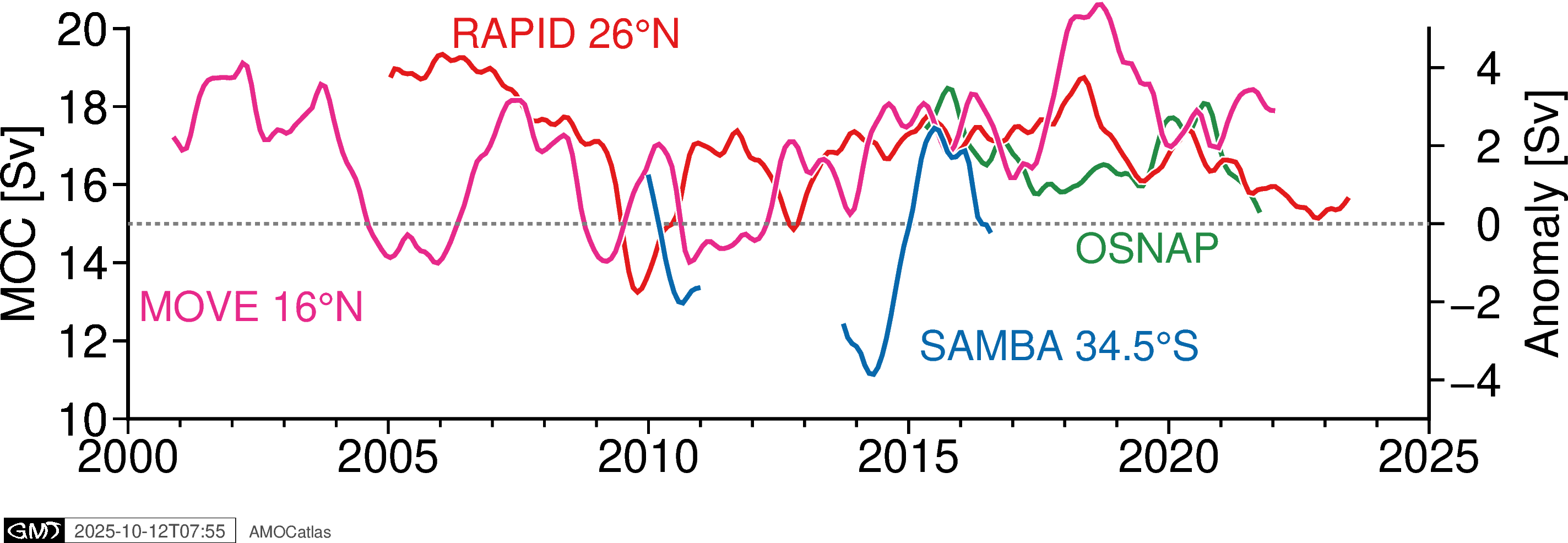
[11]:
## 8. Historical AMOC estimates from Bryden et al. 2005
[12]:
try:
fig_bryden = plotters.plot_bryden2005_pygmt()
fig_bryden.show()
# Save high-resolution version
fig_path = os.path.join(figures_dir, "bryden2005_amoc.png")
fig_bryden.savefig(fig_path, dpi=300, transparent=True)
print(f"✓ Saved: {fig_path}")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"PyGMT not available: {e}")
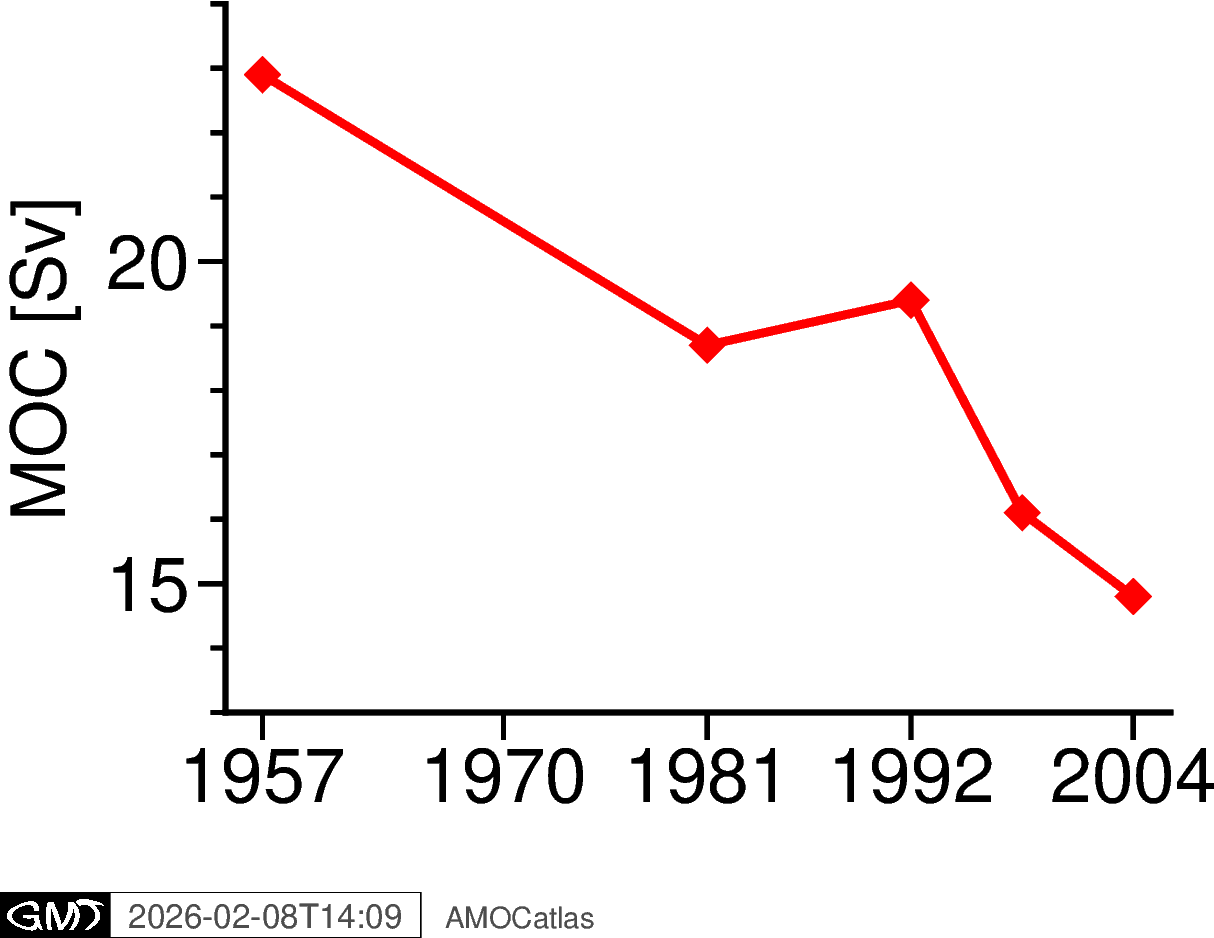
✓ Saved: ../docs/source/_static/paperfigs/bryden2005_amoc.png
9. Summary
This notebook demonstrates the streamlined workflow for creating publication-quality AMOC figures:
Data Loading: Using
read.rapid()for consistent data access and standardisationTime Series Processing: Converting to pandas with
tools.extract_time_and_time_num()Gap Handling: Using
tools.handle_samba_gaps()to prevent plotting artifactsFiltering: Applying Tukey filters with
tools.apply_tukey_filter()Visualization: Creating publication plots with
plotters.plot_*_pygmt()functions
Key Features:
Modular design using AMOCatlas functions
Optional PyGMT dependency with graceful fallback
Consistent styling across all plots
Proper handling of temporal gaps in SAMBA data
Historical context from Bryden et al. (2005)
High-resolution export capability (saved to
docs/source/_static/paperfigs/)